Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the healthcare industry, ushering in a new era of medical practices and patient care. As technology advances at an unprecedented pace, AI is becoming an increasingly integral part of healthcare systems worldwide. From enhancing diagnostic accuracy to personalizing treatment plans, AI’s potential to transform healthcare is both exciting and far-reaching. In this article, we’ll explore the current state of AI in healthcare, its applications across various medical domains, and the ethical considerations that come with this technological revolution. Join me as we dive into the fascinating world of AI-powered healthcare and its promising future.
Table of Contents
- The Current State of AI in Healthcare
- AI-Powered Diagnostics and Imaging
- Personalized Treatment Plans and Drug Discovery
- AI in Patient Care and Monitoring
- Ethical Considerations and Challenges
- The Future Outlook of AI in Healthcare
The Current State of AI in Healthcare
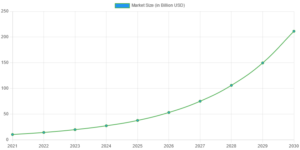
The adoption of AI in healthcare has been nothing short of remarkable in recent years. From major hospitals to small clinics, healthcare providers are increasingly turning to AI-powered solutions to enhance their services and improve patient outcomes. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global AI in healthcare market size was valued at $10.4 billion in 2021 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 38.4% from 2022 to 2030.
Key areas where AI is being implemented include:
- Medical imaging and diagnostics
- Drug discovery and development
- Virtual health assistants and chat-bots
- Predictive analytics for patient care
- Administrative workflow optimization
Dr. Eric Topol, a renowned cardiologist and digital medicine researcher, states, “AI has the potential to be the most transformative technology in the history of medicine, enabling us to see things we’ve never seen before and do things we’ve never been able to do.“
One notable success story is that of the Mayo Clinic, which implemented an AI-powered clinical decision support system to improve the diagnosis and treatment of heart disease. The system analyzes patient data, including medical history, test results, and imaging scans, to provide personalized recommendations for patient care. Since its implementation, the Mayo Clinic has reported a 30% reduction in misdiagnoses and a 25% decrease in hospital readmissions for cardiac patients.
Case Study: AI-Powered Stroke Detection at Mount Sinai Hospital
Mount Sinai Hospital in New York City implemented an AI-powered system called Viz.ai to improve stroke detection and treatment times. The system uses deep learning algorithms to analyze CT scans of patients’ brains, identifying potential stroke cases within minutes.
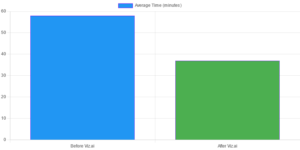
Before implementing Viz.ai, the average time from a patient’s arrival at the hospital to the start of treatment was 58 minutes. After implementation, this time was reduced to just 37 minutes – a 36% improvement. Moreover, the system’s accuracy in detecting large vessel occlusions (a type of stroke) was 95%, compared to 67% for human radiologists.
Dr. J Mocco, Director of the Cerebrovascular Center at Mount Sinai, noted, “This AI-powered system has revolutionized our stroke care. We’re now able to treat patients faster and more accurately than ever before, which can mean the difference between a full recovery and long-term disability or even death.“
The success of Viz.ai at Mount Sinai highlights the transformative potential of AI in healthcare, particularly in time-sensitive scenarios where rapid diagnosis and treatment are crucial.
AI-Powered Diagnostics and Imaging
AI is making significant strides in enhancing medical imaging analysis and diagnostics. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, AI can analyze complex medical images with remarkable speed and accuracy, often surpassing human capabilities.
Key benefits of AI in diagnostics and imaging include:
- Enhanced detection of subtle abnormalities
- Faster analysis of large volumes of imaging data
- Improved consistency and reduced human error
- Early disease detection and prevention
According to a study published in Nature Medicine, an AI model developed by Google Health achieved an accuracy of 99.3% in detecting breast cancer from mammograms, outperforming human radiologists who had an average accuracy of 98.5%.
Dr. Constance Lehman, a professor of radiology at Harvard Medical School, comments, “AI has the potential to significantly improve breast cancer screening by reducing false positives and false negatives, ultimately saving more lives through early detection.“
Case Study: AI-Powered Retinal Disease Detection
In 2018, researchers from Google AI and Moorfields Eye Hospital in London developed an AI system to detect over 50 eye diseases from retinal scans. The system was trained on a dataset of 14,884 retinal scans from 7,621 patients.
The AI system demonstrated remarkable accuracy, correctly recommending urgent referrals for sight-threatening conditions in 94% of cases, matching the performance of world-leading retina specialists. Moreover, the system provided a detailed explanation for its decisions, enhancing transparency and trust in its recommendations.
Dr. Pearse Keane, a consultant ophthalmologist at Moorfields Eye Hospital, stated, “This AI system could revolutionize the way professionals carry out eye tests. It could also help to prioritize patients who need urgent treatment, which could ultimately save sight.“
The success of this AI system in retinal disease detection showcases the potential for AI to not only match but potentially surpass human expertise in specialized medical fields, leading to earlier diagnosis and treatment of sight-threatening conditions.
Personalized Treatment Plans and Drug Discovery
AI is revolutionizing the way we approach personalized medicine and drug discovery. By analyzing vast amounts of patient data, including genetic information, medical history, and lifestyle factors, AI can help create tailored treatment plans that are more effective and have fewer side effects.
Key applications of AI in personalized medicine and drug discovery include:
- Analyzing patient data to predict treatment outcomes
- Identifying potential drug candidates for specific diseases
- Optimizing clinical trial design and patient selection
- Predicting drug interactions and side effects
A report by Accenture estimates that AI applications in drug discovery could generate up to $70 billion in savings for the pharmaceutical industry by 2028.
Dr. Daphne Koller, CEO and founder of insitro, a machine learning-driven drug discovery company, states, “AI has the potential to dramatically accelerate the drug discovery process, enabling us to bring new treatments to patients faster and at a lower cost.“
Case Study: AI-Driven COVID-19 Treatment Discovery
During the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers at BenevolentAI, a London-based AI drug discovery company, used their AI platform to identify potential treatments for the novel coronavirus. The system analyzed vast amounts of scientific literature and biomedical data to identify existing drugs that could be repurposed to treat COVID-19.
Within days, the AI system identified baricitinib, a rheumatoid arthritis drug, as a potential treatment. The drug was found to have anti-viral and anti-inflammatory properties that could help combat COVID-19. Clinical trials were rapidly initiated, and in November 2020, the FDA issued an emergency use authorization for baricitinib in combination with remdesivir for treating hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
This case demonstrates the power of AI in accelerating drug discovery and repurposing, particularly in urgent situations like the COVID-19 pandemic. The ability to quickly identify potential treatments from existing drugs can save valuable time and resources in the fight against emerging diseases.
AI in Patient Care and Monitoring
AI is increasingly being used to enhance patient care and monitoring, both in hospital settings and for remote care. From virtual health assistants to predictive analytics, AI is transforming the way healthcare providers interact with and care for their patients.
Key applications of AI in patient care and monitoring include:
- AI-powered chat-bots for initial patient triage
- Remote patient monitoring using wearable devices
- Predictive analytics to identify at-risk patients
- Enhancing electronic health records (EHR) systems
According to a survey by Accenture, 41% of healthcare executives report that they’re using AI-powered virtual health assistants to improve patient engagement and care delivery.
Dr. John Halamka, President of Mayo Clinic Platform, notes, “AI-powered tools are becoming an essential part of patient care, enabling us to provide more personalized and proactive healthcare services.“
Case Study: AI-Powered Early Warning System at Duke University Hospital
Duke University Hospital implemented an AI-powered early warning system called Sepsis Watch to detect sepsis, a life-threatening condition that can be difficult to identify in its early stages. The system analyzes patient data in real-time, including vital signs, lab results, and medical history, to predict the likelihood of sepsis development.
Since its implementation in 2018, Sepsis Watch has demonstrated remarkable results:
- 20% reduction in in-hospital mortality from sepsis
- 30% increase in compliance with sepsis treatment protocols
- 12% decrease in length of hospital stay for sepsis patients
Dr. Cara O’Brien, a hospitalist at Duke who helped develop the system, stated, “Sepsis Watch has transformed our ability to detect and treat sepsis early. It’s like having an extra set of eyes constantly monitoring our patients, allowing us to intervene before the condition becomes critical.“
This case study highlights the potential of AI in improving patient outcomes through early detection and intervention, particularly for conditions that can be challenging to diagnose in their initial stages.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges
While the potential benefits of AI in healthcare are immense, there are also significant ethical considerations and challenges that need to be addressed. As AI becomes more integrated into healthcare systems, it’s crucial to ensure that these technologies are developed and deployed responsibly.
Key ethical considerations and challenges include:
- Data privacy and security concerns
- Bias in AI algorithms and decision-making
- Transparency and explain-ability of AI systems
- Regulatory and legal challenges
- Impact on healthcare jobs and roles
A survey by KPMG found that 75% of healthcare executives believe that AI adoption in healthcare is outpacing the development of necessary privacy and security measures.
Dr. Carmel Shachar, Executive Director of the Petrie-Flom Center for Health Law Policy, Biotechnology, and Bioethics at Harvard Law School, states, “As we integrate AI into healthcare, we must ensure that these technologies are developed and deployed in ways that respect patient privacy, promote equity, and maintain human oversight.“
Case Study: Addressing Bias in Clinical Decision Support Systems
In 2019, researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, and the University of Chicago discovered racial bias in a widely used algorithm that helps hospitals and insurance companies determine which patients need extra care. The algorithm was less likely to refer Black patients for additional care than white patients with the same level of illness.
The researchers found that the bias stemmed from the algorithm’s use of healthcare costs as a proxy for health needs. Due to systemic inequalities, Black patients typically incurred lower healthcare costs than white patients with similar health problems, leading the algorithm to underestimate the health needs of Black patients.
Upon discovering this bias, the researchers worked with the algorithm’s developer to reformulate the model, reducing bias by 84%. This case highlights the importance of careful scrutiny and ongoing evaluation of AI systems in healthcare to ensure they don’t perpetuate or exacerbate existing healthcare disparities.
Dr. Ziad Obermeyer, lead author of the study, emphasized, “This is a perfect example of how AI can potentially worsen disparities in healthcare if we’re not careful. It’s crucial that we rigorously test these systems for bias and continuously work to improve them.“
The Future Outlook of AI in Healthcare
The integration of AI in healthcare represents a paradigm shift in how we approach medical diagnosis, treatment, and patient care. From enhancing diagnostic accuracy and personalizing treatment plans to revolutionizing drug discovery and improving patient monitoring, AI has the potential to transform every aspect of healthcare delivery.
As we’ve seen through various case studies and expert insights, AI is already making significant contributions to healthcare, improving patient outcomes, and increasing operational efficiency. However, it’s crucial to remember that AI is a tool to augment human expertise, not replace it. The future of healthcare lies in the synergy between human intelligence and artificial intelligence, combining the best of both worlds to provide optimal patient care.
As we move forward, it’s imperative that we address the ethical considerations and challenges associated with AI in healthcare. Ensuring data privacy, mitigating algorithmic bias, and maintaining transparency will be key to building trust and realizing the full potential of AI in healthcare.
The journey of AI in healthcare is just beginning, and the coming years promise even more groundbreaking developments. As healthcare professionals, patients, and society at large, we must stay informed, engaged, and proactive in shaping the future of AI-powered healthcare – a future that holds the promise of more precise, personalized, and accessible healthcare for all.